
Maharashtra Food security
Regional disparities along with food security have remained an issue of debate in Maharashtra ever since its inception as a State in 1960. Several studies have examined economic development as well as food security issues at the regional level, but there has been no systematic attempt made to analyse food security comprehensively taking into account its four elements viz. availability, accessibility, sustainability and utilisation. The circular argument that disparities in investment lead to underdevelopment and consequently food insecurity is a part of our larger argument. Therefore, an attempt is made in this paper to understand food security across regions of Maharashtra. The results reveal three major groups of regions in terms of food insecurity. While certain regions experience food deficit and lower poverty along with a higher level of nutritional status, the other regions exhibit higher levels of under-nutrition and poverty along with relatively higher and medium food sufficiency.
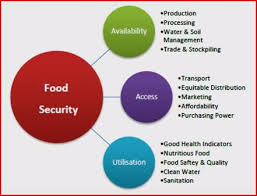
Current Sitation:-
Currently, there are various schemes being implemented by the state government which include Take Home Ration (THR) programme, public distribution system (PDS), status of Supplementary Nutrition scheme (SN) and ready-to-use therapeutic food products to severely malnourished children.Despite several schemes been implemented, the issue regarding malnourishment has not been solved. Recently the state has organised 82 medical camps with the help of private and public hospitals during which 6,481 children were checked. Of these, 2,945 children were diagnosed with moderate malnutrition and 1,493 were severely malnourished.
To eradicate malnutrition from the state, the government is likely to issue a new Government Resolution (GR) which will measuredly include creating awareness and reaching infants suffering from Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) and Moderately Acute Malnutrition (MAM).
The National Food Security Act (NFSA):-
- In 2014, Maharashtra became the eighth state to implement the National Food Security Act, which benefit seven crore people.
- The National Food Security Act (NFSA), which guarantees Right to Food to 2/3rd of the population through subsidisedfoodgrains, had implanted in Maharashtra from February 1, 2014.
- Maharashtra ranked in top 10 states in terms of the allocation of foodgrains (rice and wheat) for NFSA.
- The allocation of foodgrains (rice and wheat) for NFSA in Maharashtra was 4605.19 thousand tonnes during 2015-16. It was 15.91% of the allocation of foodgrains (rice and wheat) for NFSA in India during 2015-16.
Public distribution System and other schemes related to food securtiy:-
Targeted Public Distribution System
Under the Minimum Common Need Programme of Government of India, the poor families in the State were provided food grains at subsidized rate w. e. f. 1 st June, 1997. BPL Yellow rationcard holders are provided with 35 Kgsfoodgrains (Wheat + Rice) and APL Saffron rationcard holders are provided with 15 Kgsfoodgrains (Wheat + Rice )
Tricolor Ration Cards Scheme
The affluent families do not purchase foodgrains under PDS and therefore with a view to curb diversion of foodgrains and provide more foodgrains to the needy families, the State Govt. introduced Tricolor ration card scheme w. e. f. 1st May, 1999. Accordingly, as per following criterias 3 different colored ration cards are issued in the State :-
Yellow Ration Cards
Under Targeted Public Distribution System the following criteria are applied :-
- Families having annual income up to Rs. 15,000/- having been included in IRDP List of 1997-98.
- None of the members in the family should be a doctor or a lawyer or an architect or a chartered accountant.
- None of the members in the family should be a professional tax payer, a sales tax payer or an income tax payer or eligible to pay such tax.
- The family should not posses residential telephone.
- The family should not posses four wheeler vehicle.
- None of the family members should hold total two hectare rain fed or one hectare semi-irrigated or 1/2 hectare irrigated (double in drought prone talukas) land.
- The Govt. has taken decision to issue BPL Ration Card, on temporary basis to all the Vidi workers, all members of Pardhi&Kolhati community vide GR dated 9.9.2008.
- The Govt. has taken decision to issue BPL Ration Card, on temporary basis to the Abandoned women vide G.R. dated 29.9.2008 & 21.2.2009 and amendment has been made to the same vide G.R. dated 17.1.2011
- The Govt. has taken decision to issue BPL Ration Card on temporary basis to all the non-working cloth mills,cotton mills & sugar factories workers vide GR dated 17.3.2003.
Antyodaya Anna Yojana(AAY)
In the state Antyodaya Anna Yojana has been started w.e.f. 1st May 2001 Under this scheme 35 Kgsfoodgrains( Wheat at the rate- Rs. 2.00 per Kg+ Rice at rate Rs. 3.00 per Kg ) is distributed to the AAY cardholders.
Under this scheme the families are selected from following BPL categories..
- Land less agriculture labourers, marginal farmers, rural artisans/ craftsmen such as potters, tanners, weavers, blacksmiths, carpenters, slum dwellers and persons earning their livelihood on daily basis in the informal sector like porters, coolies, rickshaw pullers, hand cart pullers, fruit and flower sellers, snake charmers, rag pickers, cobblers, destitutes and other similar categories in both rural and urban areas>
- Households headed by Widows or Terminally ill persons or disabled persons or persons aged 60 years or more with no assured means of subsistence or social support
- Single widows or terminally ill persons or disabled persons or persons aged 60 years or more with no assured means of subsistence or societal support
- All Primitive Tribal Households ( Madia, Kolam, katkari)
- Household headed by leprosy patients or recovered leprosy patients are eligible to get benefits under this scheme
- While distributing AAY ration cards to eligible families, priority given to HIV/AIDS affected persons
Criteria For Saffron Ration Cards
- Families having total annual income of more than Rs. 15,000 and less than 1 lakh.
- None of the members in the family should have four wheeler mechanical vehicle (excluding taxi- driver).
- The family in all should not posses four hectare or more irrigated land.
Criteria For White Ration Cards
The families having annual income of Rs. 1 Lakh or above, any member of the family possessing a four wheeler or the family aggregately holding more than 4 hectare irrigated land are issued white ration cards.
Annapurna Scheme
“Annapurna scheme” is being implemented in this State w.e.f. 1st April, 2001. This is 100% centrally sponsored scheme. Under this scheme 10 Kgs of foodgrains per month are provided free of cost to the old destitute people of 65 years and above age. The main eligibility criteria for the benefit of this scheme is that the person should not be in receipt of pension under the National old age pension scheme or state pension scheme.
Scheme regarding Distribution of Food grains at BPL rate to Welfare Institutes, Hostels etc. (Establishment Cards)
Central Government sanctions additional allocation of foodgrains (Wheat & Rice) at BPL rate for distributing it to Welfare Institutes in the State. Accordingly food grains are distributed as per GR dated 26.4.2002.Under the said scheme 15 Kgs. foodgrains per month per cardholder are distributed only to Establishment Ration Cardholders within limit of the received allocation.
Scheme of distribution of subsidised imported Palm Oil–(during 2011-2012)
The scheme of distribution of subsidised imported Palm Oil is being implemented in the State. The GOI has sanctioned total allocation of 87,740 MT Palm oil for the State for the period from April, 2011 to September, 2011. This palm oil is being distributed to the beneficiaries in the State for the period from July, 2011 to December, 2011. Under this scheme 1 litre Palm Oil per beneficiary (i.e. per card) per month is being distributed at the subsidised rate of Rs. 45/- per litre to BPL, AAY, APL& Annapurna Beneficiaries in the State.
Levy Sugar Distribution Scheme
In February 2001 the Government of India decided to restrict the distribution of levy sugar only to the families below poverty line. Accordingly, levy sugar is being distributed amongst below poverty line families through the Public Distribution System. In order to make available more sugar to below poverty line families through the public distribution system, the quantum has been increased from 425 gms. to 500 gms per person per month. The central Government prescribes the retail issue price of levy sugar through the Public Distribution System. The retail issue price of levy sugar is Rs.13.50 per Kg w.e.f. 1.3.2002.
PDS Kerosene Allocation And Distribution
From April 1999 to January, 2000 the state Government had received allocation of 1,68,972 K.L.s Kerosene per month from central Government. From April 2010 to May 2011 the allocation received was 1, 30,356 KL per month. It is again further reduced in June 2011 and April, 2012. Up to March, 2013 State Government has received allocation of 75,648 K.L.s. Kerosene per month from Central Government. Beyond this now from April 2013 the additional reduction of 19.50% has resulted in availability of only 34% (60,864 K.L.) of kerosene requirement of the state.
Rates of wholesale & Retail Kerosene
As per the directions of the State Govt. rates of wholesale & retail kerosene, are finalised by Collector at District level & Controller of Rationing in Mumbai & Thane Rationing Area. At present the retail price of kerosene in Mumbai / Thane Rationing Area is Rs.15.05 per litre and in other districts it comes between Rs.15.05 to Rs.16.22 per litre.
Special subsidised rate of Kerosene
As per the policy of Central Government since 16th June 1988 a special subsidised rate is made applicable to the kerosene sold in hilly areas of the State. This scheme has been started in the 11 districts and 62 talukas. The 11 districts are Dhule, Nashik, Thane, Pune, Satara, Ratnagiri, Sindhudurg, Sangli, Kolhapur, Ahmednagar&Raigad.
Measures have been taken to avoid misuse of kerosene
- In order to differentiate the PDS Kerosene the colour of the kerosene to be distributed under PDS has been made blue. This helps to prevent misuse of PDS kerosene.
- PDS Kerosene is distributed only on ration cards. For this instructions are issued to all Collectors to issue ration cards to those who do not have the same and appoint retailers in villages.
- In order to avoid diversion of kerosene by retailers, instructions have been issued to supply kerosene to retailers at their doorstep at least in 50% villages of the districts.
- Instructions have been issued to all Collectors to monitor & stream lining of kerosene distribution system. Accordingly periodical and surprise inspections of kerosene licensees are carried out. Also sudden and surprise visits or raids are made on kerosene licenses or petrol/diesel pumps. Necessary action is taken against those who are found guilty.
Door Step Delivery Scheme Under Public Distribution System
The scheme of Door Step Delivery is being implemented in the tribal, remote and DPAP areas wherein the transportation of the commodities is carried out from government godowns up to door step of fair price shops by the government vehicles and at the government cost.
In tribal areas, this scheme is being implemented through the Maharashtra State Co-operative Tribal Development Corporation Limited, while in DPAP areas it is implemented through Maharashtra State Co-operative Marketing Federation Limited. The Corporation and the Federation are reimbursed for running cost of the scheme @ Rs.15.00 and Rs.13.00 per Quintal, respectively
Minimum Support Price Scheme
The Minimum Support Price (MSP) Scheme is a scheme of the Government of India (GOI) to safeguard the interests of the farmers. Under this Scheme the GOI declares the minimum support Prices of various agricultural produces and assures the farmers that their agricultural produce (of FAQ) will be purchased at the MSP, thereby preventing its distress sale. The Food Corporation of India (FCI) acts as the Nodal Agency of the GOI. On behalf of FCI, in Maharashtra, the MSP Scheme is implemented through the State agencies.
Recently The Maharashtra government launched Aadhaar-linked ration at fair price shops across the state by March 31. Aadhaar card holders will have to record their thumbprints at biometric machines set up in ration shops to access subsidized grain available under the Food Security Act.
Maharashtra Government is one of the front runners in this initiative and intends to repair the flaw by introducing technology solution in this food supply and distribution system. An Expression of Interest (EOI) was published by the state government which attracted interest of five bidders that included TCS, CMC, CMS and ECIL along with Spanco. In 2009, TCS and Spanco were short listed as the final contenders on technology grounds and the project was bagged by Spanco (PPP model) on BOOT basis for 3 years. The total size of the project was about INR 250 crores. The scope of the contract is to computerize the entire ration distribution system and introduce new technology in order to stop pilferage in the system, so that the subsidized item reaches the needy.
MPSC Notes brings Prelims and Mains programs for MPSC Prelims and MPSC Mains Exam preparation. Various Programs initiated by MPSC Notes are as follows:-- MPSC Mains Tests and Notes Program
- MPSC Prelims Exam 2020- Test Series and Notes Program
- MPSC Prelims and Mains Tests Series and Notes Program
- MPSC Detailed Complete Prelims Notes